 \\
\\
Summary module description:
Aims:
To introduce the human from a cybernetics viewpoint, in particular to look at the engineering of humans and of assistive machines.
Assessable learning outcomes:
By the end of this module the students should be able to understand:
- basic human biomechanics and the neural controller
- simple models of the muscles, tendons, neurons, proprioceptors and other elements associated with movements.
- force/torque and their relationship to angular accelerations
- the response of materials, including biomaterials to forces and torques
- the control and cybernetics involved in movement
- applications across all areas of biomedical engineering
Additional outcomes:
Outline content:
The course will look at how humans and animals move. This will include the sensory mechanisms that monitor movement, the muscles and the spinal reflex, and hypothesised mechanisms as to how the brain direct movements. Movement patterns considered will include animal gaits, minimum jerk methods, cerebellum predictors and the equilibrium point hypothesis. Applications to prosthetics, orthotics, exoskeletons, and wearables will be explored.
| Written exam (open book) | 35 |
| Report (and 3 minute presentation) | 15 |
| Soft technologies (Dr Hayashi) | 50 |
Lecture notes will be updated each week to include the new weeks content
Report and presentations
To be discussed
Formative assessment
- Option for a formative assessment to give an overview of what might be expected in the exam.
Topics that may be included
- Anatomy
- Statics, joints (pin, sliding, revolute) pin jointed trusses
- Energy (Hamiltonian systems)
- Dynamics; Gait (running and walking), sports and performance
- Beams/beam theory (Bones)
- Materials (biological and engineering)
- Engineering failures
- Haptics
- Prosthetics
- Rehabilitation and assistive robotics
- Cognitive systems : Reflex, brain models etc
- Prediction (Wolpert)
- Conservation of Energy, momentum, angular momentum, mass
- Coordinate frames, centre of mass, moment of inertia, effects of scale
- Muscle models
- Perception (e.g. arm length/Fraser and wing)
- Newton and Newton-Euler
- Fluids - Dimensional analysis
- Internal models
- Serial and parallel chain linkages
Books
Academic papers will also be used to cover e.g.Valero-Cuevas[valero2003towards]. Key papers should either be available via the university library, online or on blackboard.
Biomechanics
The words
| Bioengineering | Engineering |
| Biomedical engineering | Medical Engineering |
| Biomechanics | Mechanics |
| Biophysics | Physics |
| Biochemical | Chemical |
| Biofeedback | Feedback |
| Biotechnology | Technology |
| Biocybernetic | Cybernetic |
| Biosphere |
| Biorhythmn |
| Biological |
| Bionic |
Look up these words and assess how you identify with the areas they describe.
Definitions
- Prosthetic (external, implants)
- Orthotic (external, implants)
- Exoskeleton
- Rehabilitation aid
- Assistive aid
- (please expand)
Anatomical overview
Anatomical directions, movements and planes
- Extension/Flexion
- Proximal/distal
- Superior/inferior
- posteria (behind)/anterior (in front of)
- dorsal(towards the spine)/ventral(towards the belly)
- Medial(to the middle)/lateral (to the side)
- Bilateral/unilateral
- ipsilateral (same size as)/contralateral (oposite side)
- (please cross check and expand)
See also (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anatomical_terms_of_location) and (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Anatomical_plane)
Identify
- Sagittal (longitudinal) plane
- Parasagittal
- Horizontal (axial or transverse) plane
- Coronal (frontal) plane
Why is it called the Saggital or Coronal plane?
Degrees of freedom
- A spacial mechanisms exist in 3D space and can uniquely fix a coordinate frame with up to 6 degrees of freedom (3 positions, 3 orientations)
- A planar mechanisms exist in a plane and can uniquely fix a coordinate frame with up to 3 degrees of freedom (2 positions, 1 orientation)
- Serial chains
- e.g. most extremities (arms/legs)
- Parallel chains
- e.g. rib cage
- Steward platform
- mixed
- e.g. delta robot
- An active degree of freedom is a joint that is associated with an actuator.
- In a serial chain, $n$ active degrees of freedom can be linked with at least $n$ actuators (for example most joints have extensor and flexor muscles)
- If $n$ degrees of freedom are linked to fewer than $n$ actuators at least one degree of freedom must be passive.
The lower joint pairs (The 6 Reuleaux pairs)
Lower pairs are joints where the two suface constraints remain in contact.
| Name (Symbol) | DoF | contains | type | example |
| Revolute (R) | 1 | R | planar | a pin joint or hinge |
| Prismatic (P) | 1 | P | planar | a drawer |
| Helical (H) | 1 | R+P | 3D | a screw or a nut and bolt |
| Cylindrical (C) | 2 | R+P | 3D | a radio aerial |
| Spherical (S) | 3 | 3R | 3D | shoulder |
| Sliding/Flat (F) | 3 | R+2P | 3D | knee |
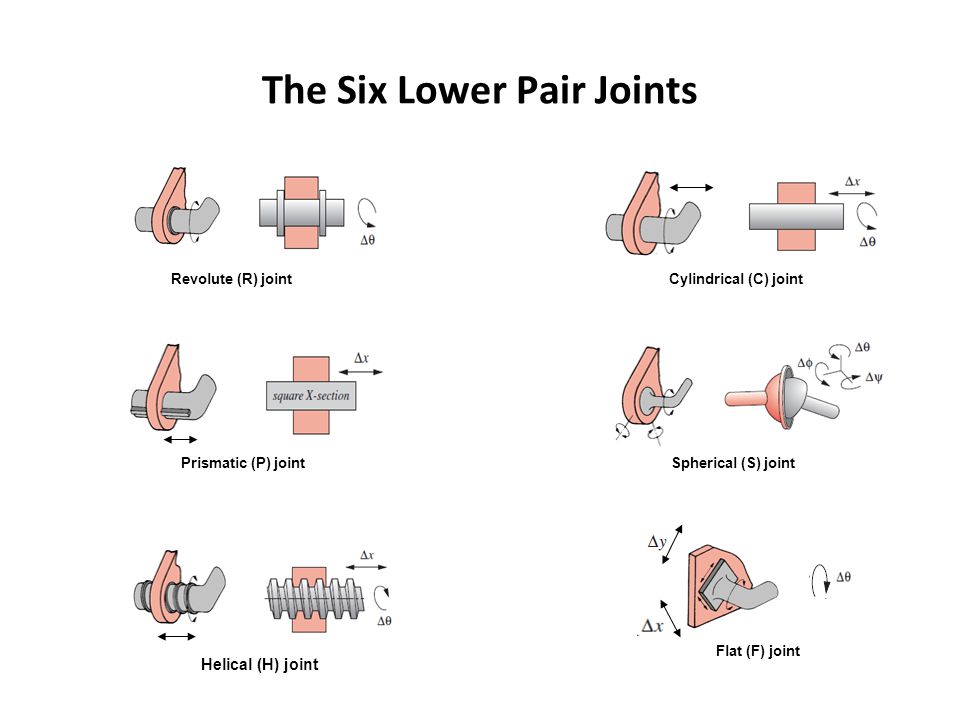
The screw joint can be considered as the most general robot joint. All rigid motion of links in a robot can be described as a combination of screw motions.
Question, how does a screw joint represent
- a revolute joint
- a prismatic joint?
Anatomical joints

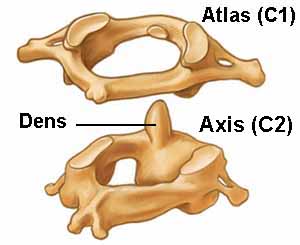
- The Atlas is the first bone in the spine (C1) that supports the skull.
- The Axis is the bone immediately below (C2) that enables the head to rotate left/right.
- Forward and backwards, and sizeways movements of the head are distributed along C2 to C7
W.S. Harwin 24/9/2023